Fire360: Robust Perception & Episodic Memory in Degraded 360° Firefighting Video
A large-scale benchmark of 360° firefighter training videos that probes spatial grounding, temporal understanding, safety-critical reasoning, and transformation-invariant retrieval in the environments where reliability matters most.
Overview
Each year, tens of thousands of firefighters are injured in the line of duty, often when visibility is severely reduced and situational perception breaks down. Existing video benchmarks typically assume clean, forward-facing views or synthetic scenes, which makes it difficult to study model behavior in degraded 360° environments where decisions have direct safety implications.
Fire360 is constructed from professionally recorded firefighter training sessions with certified instructors and covers indoor rescues and outdoor operations across day, night, dense smoke, and post-fire overhaul. The benchmark defines five tasks (visual question answering, temporal captioning, object localization, safety-critical reasoning, and transformed object retrieval) in order to isolate where human experts retain robust understanding and state-of-the-art multimodal models still fail.
Dataset

Fire360 complements prior video resources by jointly offering 360° views, egocentric and third-person perspectives, synchronized audio, and explicitly safety-critical events.
| Dataset | Third-Person | 360° | Egocentric | Video | Audio | Real-world | Safety-Critical | Duration (s) | Public |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ego4D | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | 10,800,000 | ✓ |
| EPIC-Kitchens | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | 712,800 | ✓ |
| 360+x | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 244,800 | ✓ |
| HACS++ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 500,400 | ✓ |
| Fire360 (Ours) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 180,000 | ✓ |
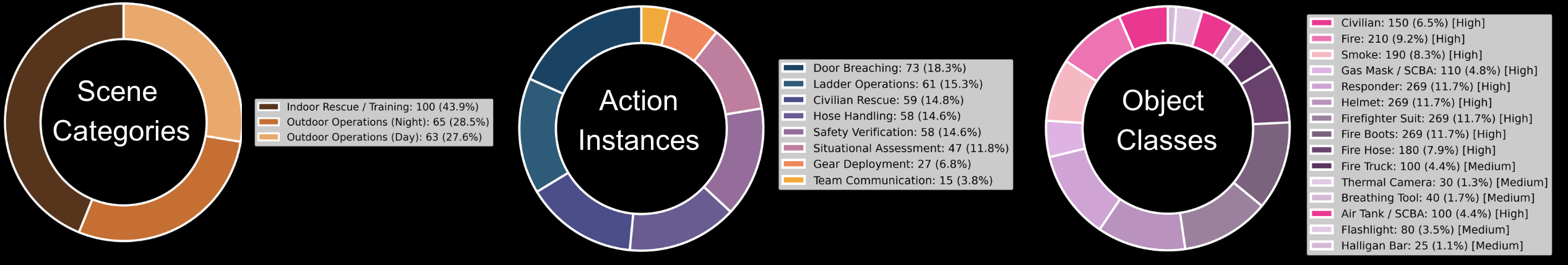
Fire360 balances indoor rescue/training (43.9%) with outdoor operations at night (28.5%) and outdoor operations during the day (27.6%), ensuring that models must handle both low-light interiors and open-air incident grounds. Eight safety-relevant action categories support temporal reasoning and analysis of model failure modes.
Benchmark Tasks
Models answer expert-authored questions about presence, visibility, and protocol adherence in single equirectangular frames (e.g., “Is a clear egress path visible through the smoke?”).
Given short degraded clips, models must describe what firefighters are doing in natural language, aligned with standardized training procedures.
Category-agnostic localization of safety gear (SCBA, helmets, hoses) in 360° equirectangular frames, where poles exhibit strong geometric distortion.
Models decide whether a frame/clip is safe and justify their decision using a firefighter checklist (e.g., sealed gas mask, three-point contact on ladders).
Given a clean exemplar of an object (helmet, hose, extinguisher) and an unpaired 360° scene after fire damage, the model must retrieve the degraded instance without seeing the transformation.
Transformed Object Retrieval (TOR)
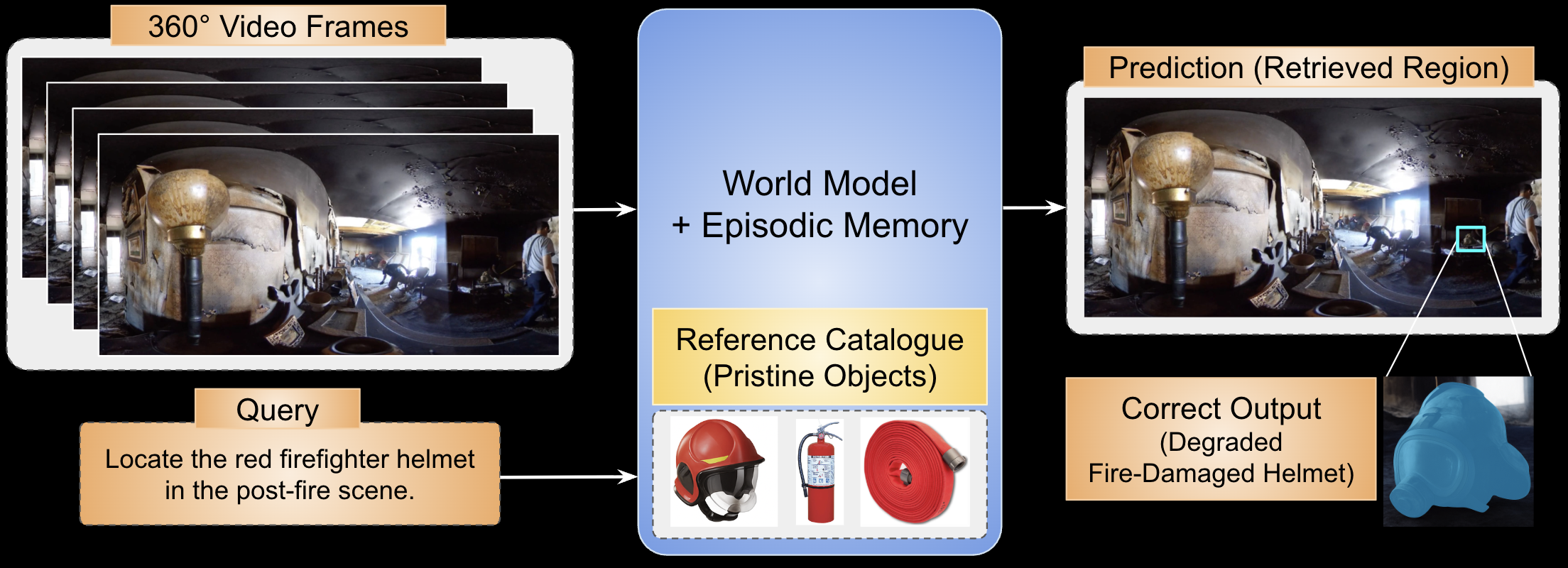
In a typical example, the reference catalogue provides a clean side view of a red firefighter helmet. The target frame shows the same helmet after an interior room burn: the visor is blackened, reflections are gone, and surrounding walls have collapsed. Pipes, lamps, and other round shapes now compete as distractors.
Humans successfully retrieve the correct region in 83.5% of cases. GPT-4o achieves only 39.8%, often confusing pipes or background clutter for the helmet. CLIP and BLIP-2 perform worse, revealing that current models lack transformation-invariant object identity when temporal continuity is removed.
Results
Bar plots summarize the persistent human–model gaps across all five Fire360 tasks. Even state-of-the-art systems fall far short of expert performance when faced with smoke, darkness, and 360° distortion.
View detailed tabular results
For each task, the highlighted row indicates the best-performing model across all evaluated systems.
| Model | Score | Human | Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Task: Visual Question Answering (VQA) | |||
| GPT-4o | 53.8% | 91.4% | Top-1 accuracy |
| Qwen-VL | 47.2% | 91.4% | Top-1 accuracy |
| LLaVA-v1.5-13B | 50.3% | 91.4% | Top-1 accuracy |
| BLIP-2 (OPT-6.7B) | 42.7% | 91.4% | Top-1 accuracy |
| InstructBLIP | 48.6% | 91.4% | Top-1 accuracy |
| Kosmos-2.5 | 47.5% | 91.4% | Top-1 accuracy |
| Task: Temporal Action Captioning | |||
| GLaMM-7B | 0.341 | 0.85 | BLEU-4 |
| SwinBERT | 0.315 | 0.85 | BLEU-4 |
| ProgressCaptioner | 0.288 | 0.85 | BLEU-4 |
| Task: Object Localization under Distortion | |||
| Grounding DINO | 38.4% | 85.2% | Mean IoU |
| OWLv2 | 39.8% | 85.2% | Mean IoU |
| YOLO-World | 36.5% | 85.2% | Mean IoU |
| Task: Safety-Critical Reasoning | |||
| GPT-4o (prompted) | 28.9% | 94.6% | Checklist accuracy |
| Qwen-VL | 32.5% | 94.6% | Checklist accuracy |
| Claude-3 Sonnet | 33.0% | 94.6% | Checklist accuracy |
| Llama-Guard-3-8B | 27.4% | 94.6% | Checklist accuracy |
| Task: Transformed Object Retrieval (TOR) | |||
| GPT-4o | 39.8% | 83.5% | Retrieval accuracy |
| CLIP (ViT-B/32) | 32.5% | 83.5% | Retrieval accuracy |
| BLIP-2 (OPT-6.7B) | 35.1% | 83.5% | Retrieval accuracy |
| CoLLM | 35.7% | 83.5% | Retrieval accuracy |
| MCoT-RE | 33.5% | 83.5% | Retrieval accuracy |
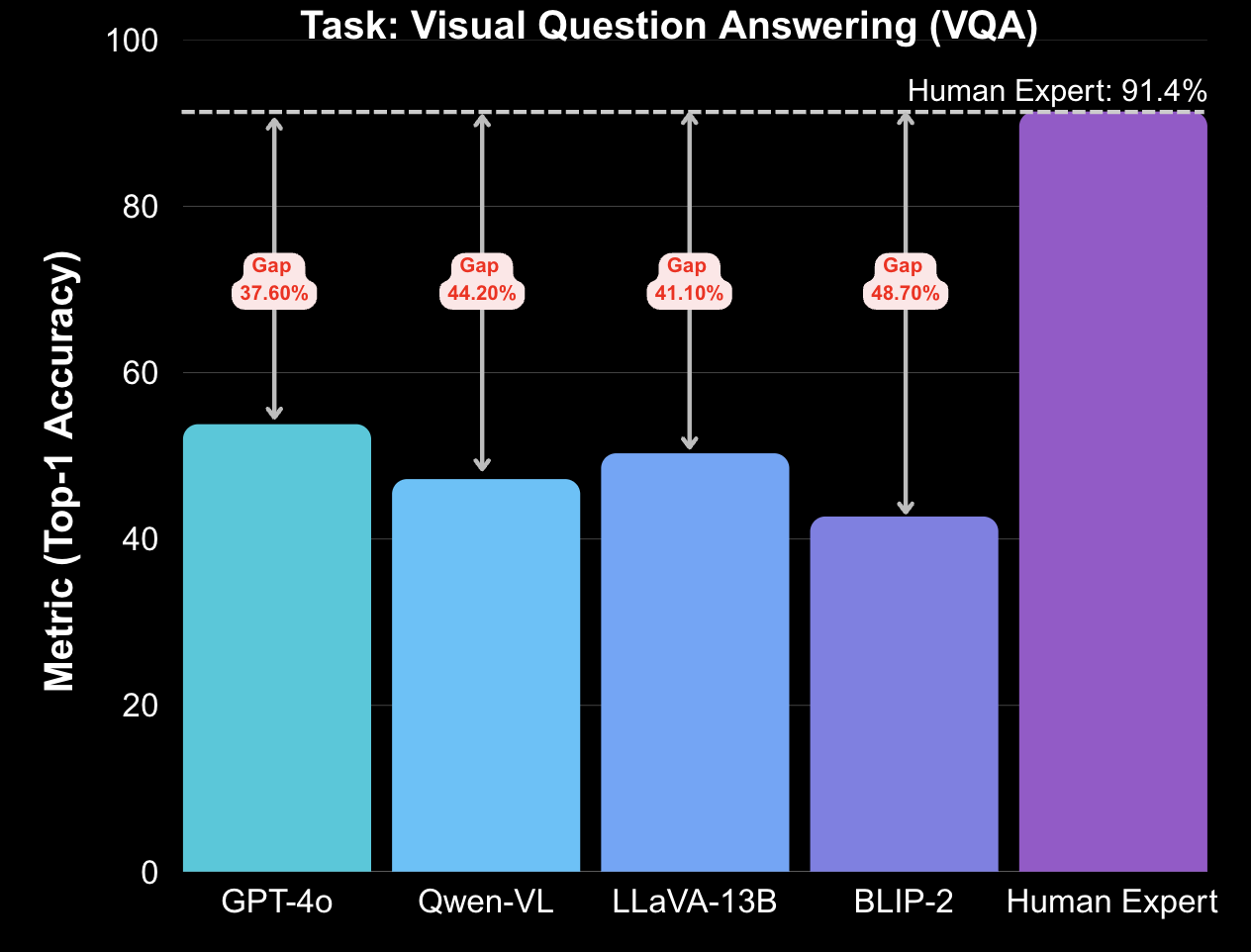
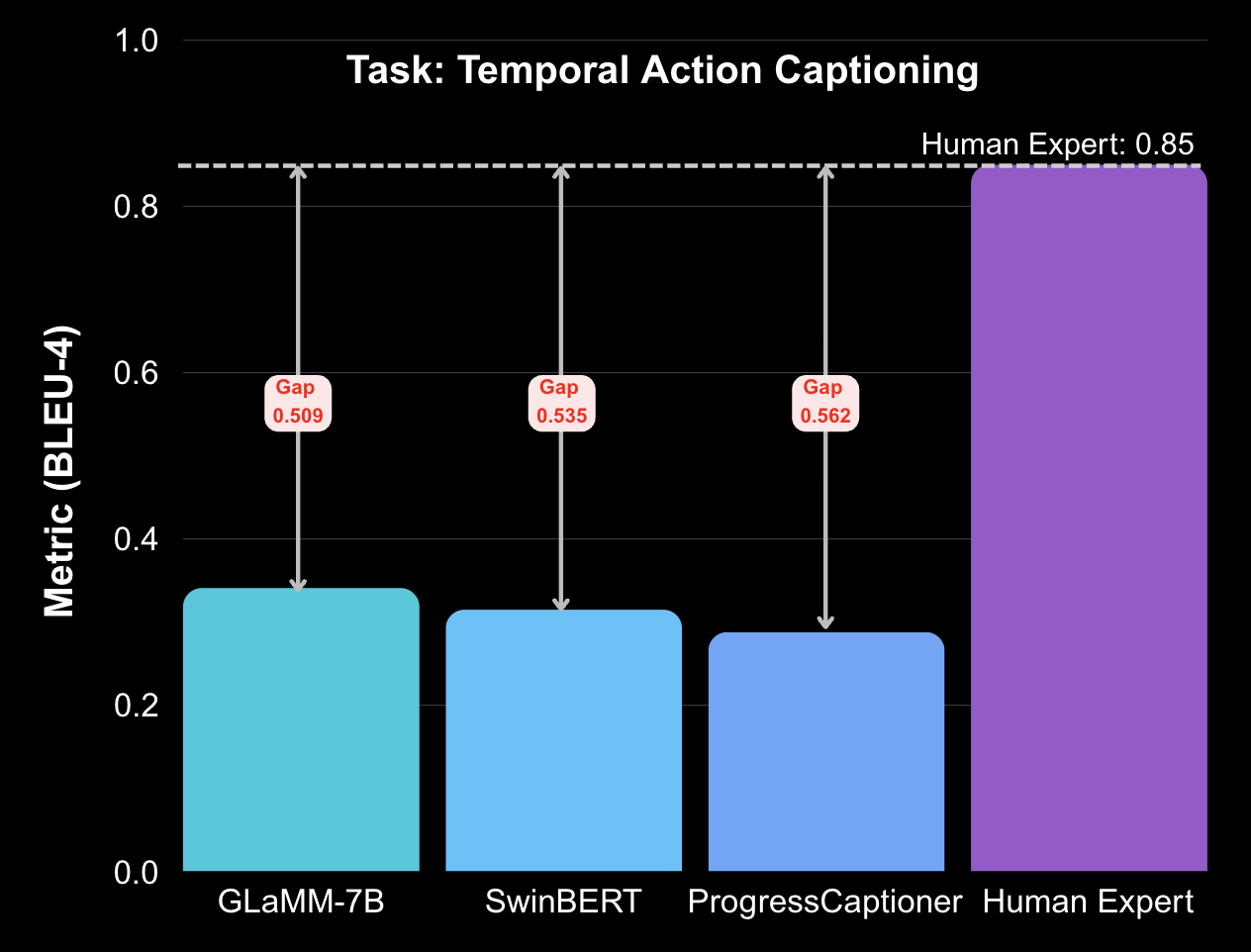
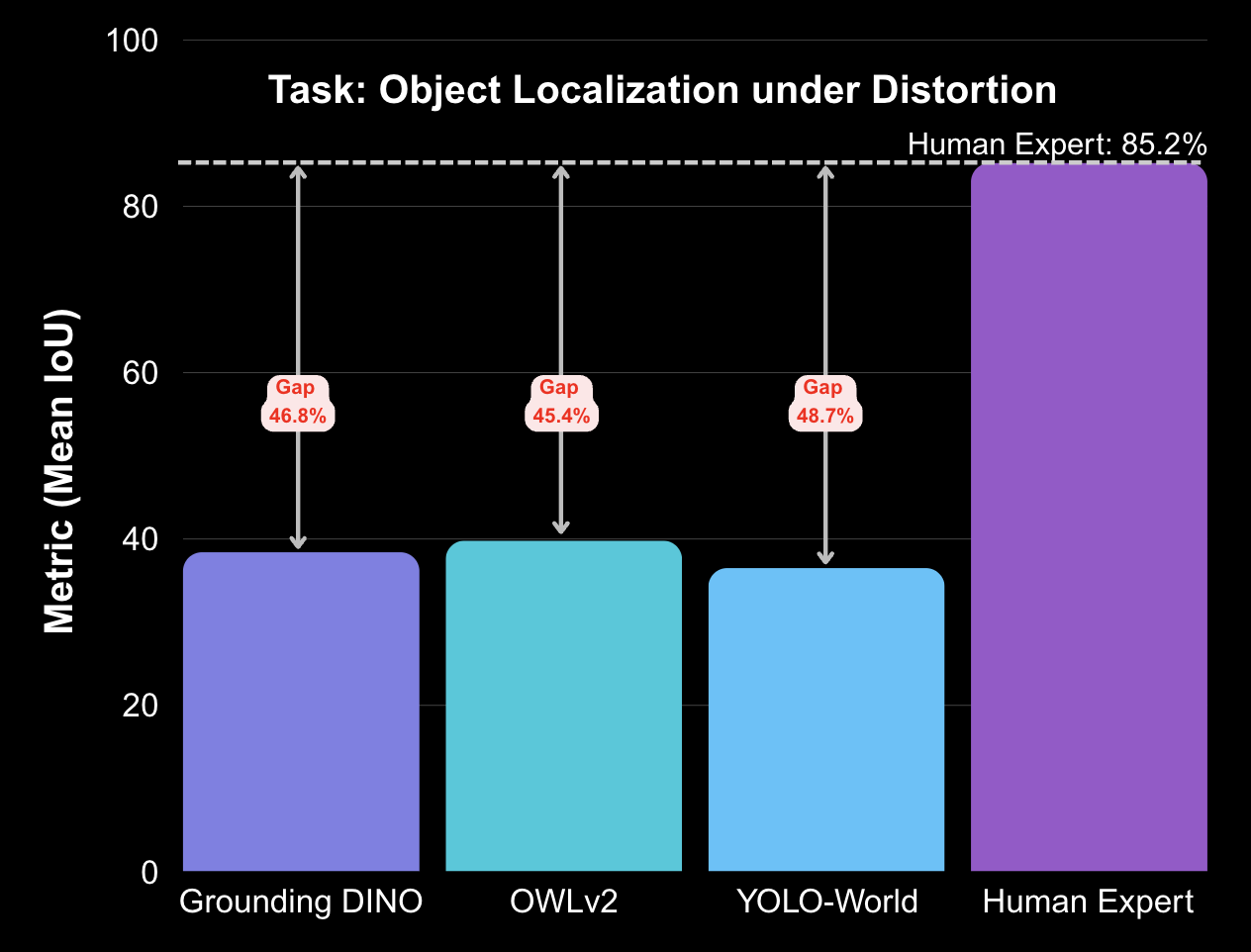
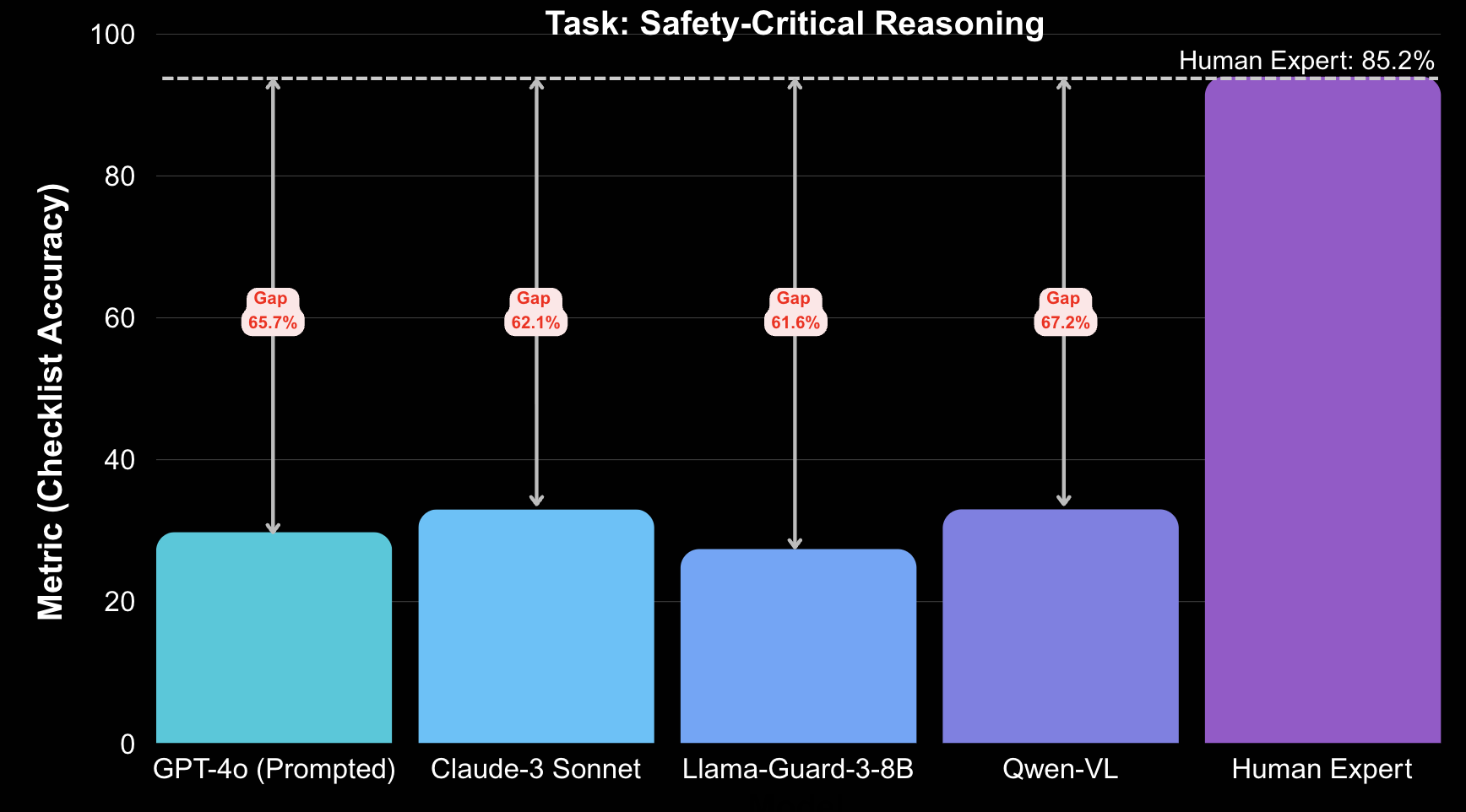
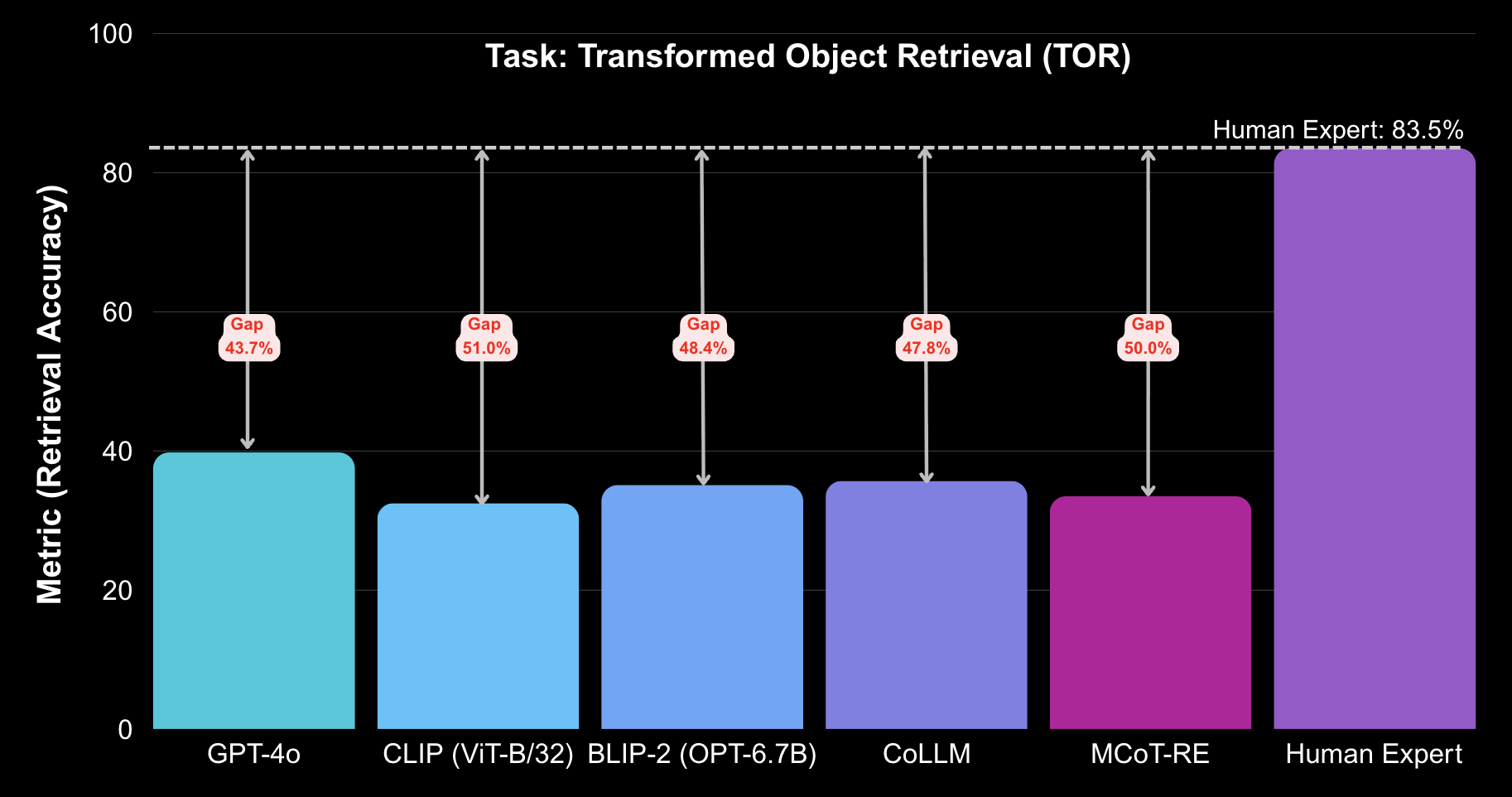
Together, these plots and tables highlight a consistent pattern: Fire360 exposes large, degradation-driven failures across architectures and tasks, indicating that robust perception and episodic memory in 360° emergency scenes remain very open problems for current multimodal models.
Ethics and Bibtex
All footage documents professional training drills with informed consent. No personally identifiable information is included; participants appear in protective gear. Fire360 is released for research on robust, safety-critical multimodal systems and may not be used for surveillance, profiling, or non-consensual monitoring.
@misc{tiwari2025fire360benchmarkrobustperception,
title = {Fire360: A Benchmark for Robust Perception and Episodic Memory
in Degraded 360-Degree Firefighting Videos},
author = {Aditi Tiwari and Farzaneh Masoud and Dac Trong Nguyen
and Jill Kraft and Heng Ji and Klara Nahrstedt},
year = {2025},
eprint = {2506.02167},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
primaryClass = {cs.CV},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.02167},
}